Running large language models (LLMs) locally offers enhanced privacy, greater control, and eliminates subscription costs. Historically, this often meant sacrificing output quality. However, recent open-weight models, such as OpenAI’s gpt-oss and Alibaba’s Qwen 3, now operate directly on PCs, providing high-quality results, particularly for local agentic AI applications.
This development creates new possibilities for students, hobbyists, and developers to explore generative AI applications on their local machines. NVIDIA RTX PCs enhance these experiences, providing rapid and responsive AI performance.
Getting Started With Local LLMs Optimized for RTX PCs
Leading LLM applications have been optimized for RTX PCs, leveraging the full performance capabilities of Tensor Cores within RTX GPUs.
An accessible method for beginning AI on a PC involves Ollama, an open-source tool offering a straightforward interface for operating and interacting with LLMs. It facilitates features like dragging and dropping PDFs into prompts, conversational chat, and multimodal understanding workflows that incorporate both text and images.
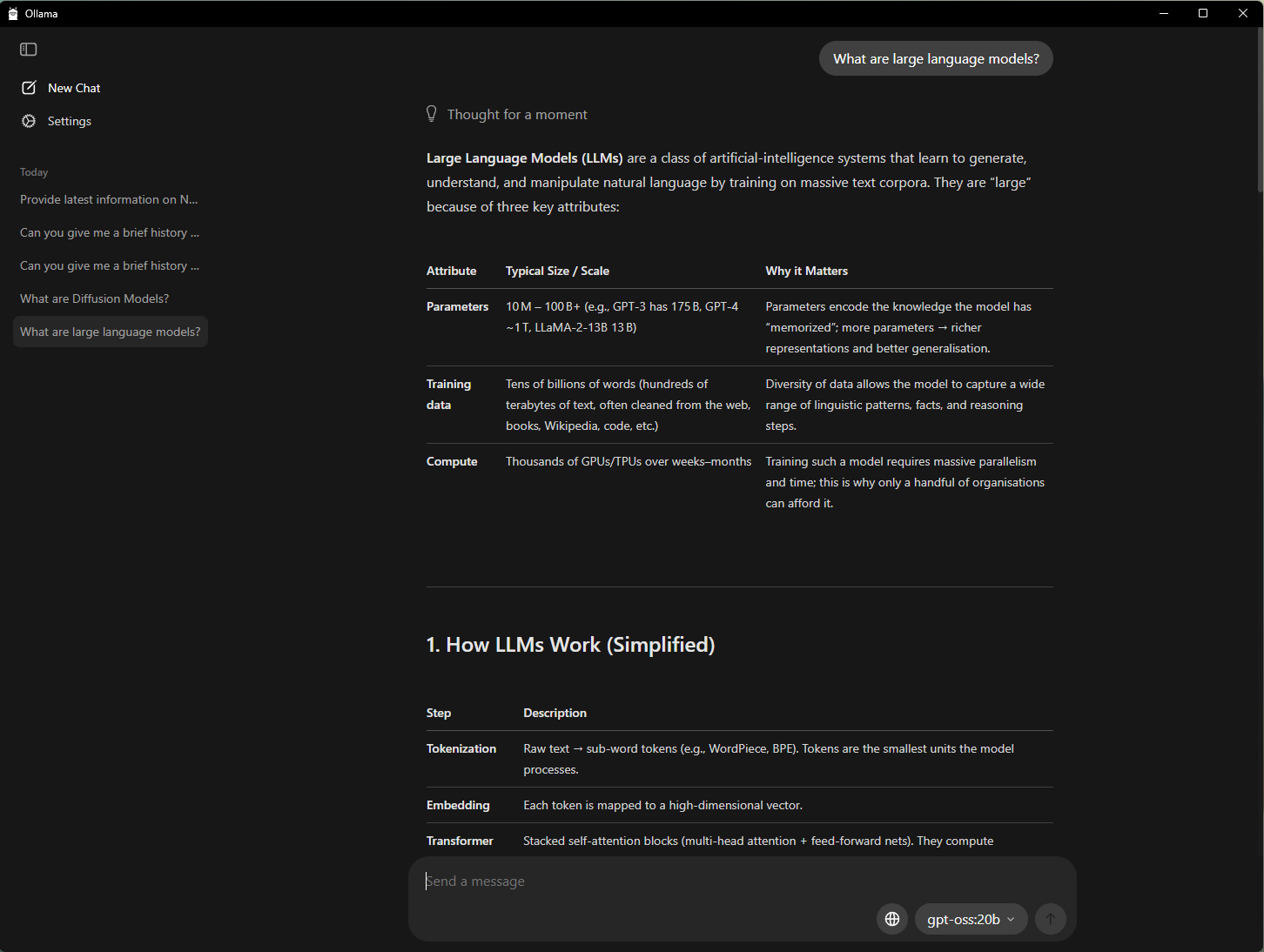 Ollama simplifies generating answers from basic text prompts.
Ollama simplifies generating answers from basic text prompts.
Ollama’s performance and user experience on GeForce RTX GPUs have seen improvements through collaboration. Recent updates include:
- 50% performance increase for OpenAI’s gpt-oss-20B model.
- 60% performance increase for the new Gemma 3 270M and EmbeddingGemma models, enhancing RAG efficiency.
- An optimized model scheduling system for better memory utilization reporting.
- Stability improvements to minimize crashes.
Ollama functions as a developer framework compatible with other applications. For instance, AnythingLLM — an open-source application enabling users to create custom AI assistants with any LLM — can operate using Ollama and leverage its accelerations.
Individuals can also begin using local LLMs via LM Studio, an application built on the widely used llama.cpp framework. This app offers a user-friendly interface for local model execution, allowing users to load various LLMs, engage in real-time chat, and even expose them as local API endpoints for custom project integration.
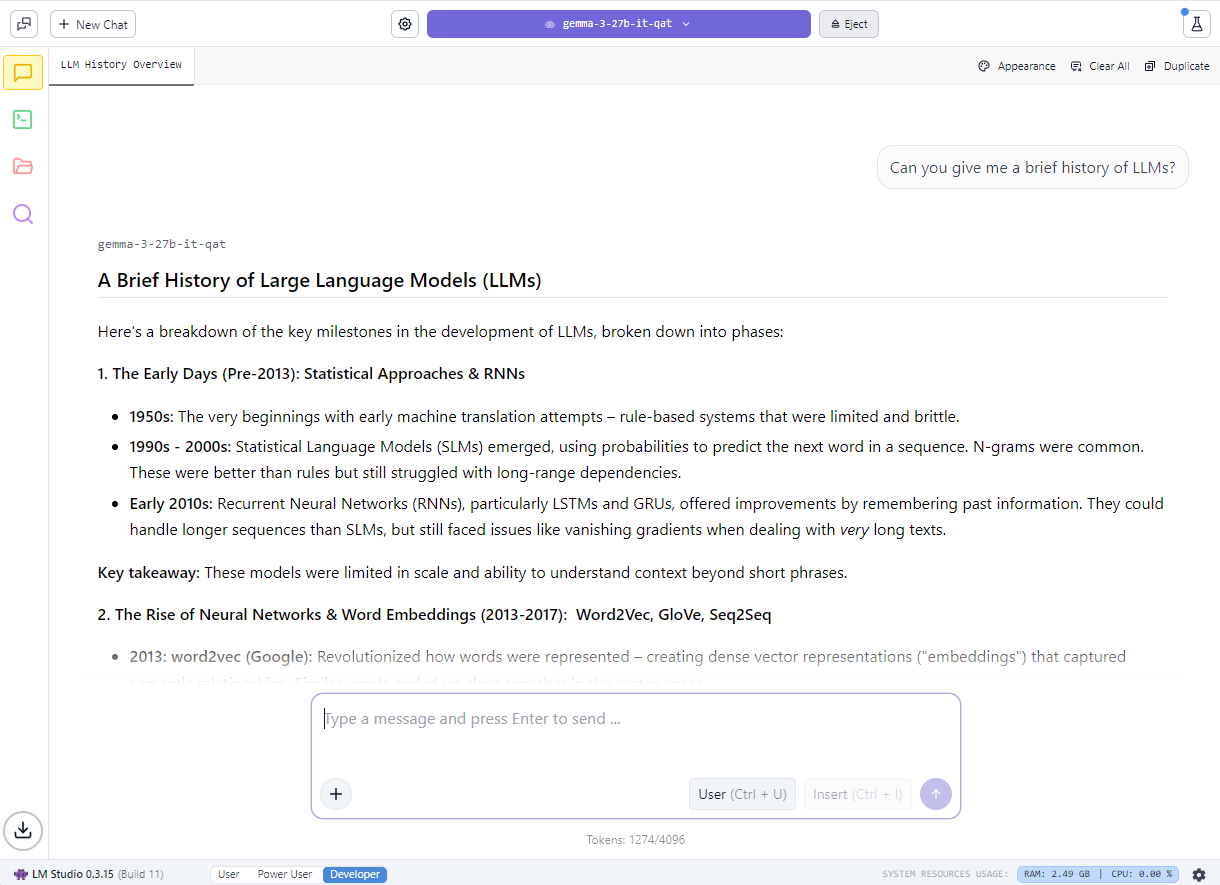 An example of LM Studio generating notes, accelerated by NVIDIA RTX.
An example of LM Studio generating notes, accelerated by NVIDIA RTX.
Performance on NVIDIA RTX GPUs has been optimized through collaboration with llama.cpp. Recent updates feature:
- Support for the latest NVIDIA Nemotron Nano v2 9B model, utilizing a hybrid-mamba architecture.
- Flash Attention enabled by default, providing up to a 20% performance boost.
- CUDA kernel optimizations for RMS Norm and fast-div based modulo, leading to up to 9% performance gains for common models.
- Semantic versioning, simplifying future release adoption for developers.
Further details are available regarding gpt-oss on RTX and the collaboration with LM Studio to enhance LLM performance on RTX PCs.
Creating an AI-Powered Study Buddy With AnythingLLM
Beyond improved privacy and performance, local LLM execution eliminates limitations on file quantity and availability duration. This allows for extended context-aware AI conversations, offering greater flexibility in developing conversational and generative AI assistants.
Students often face challenges managing numerous slides, notes, labs, and past exams. Local LLMs provide a solution by enabling the creation of personalized tutors capable of adapting to specific learning requirements.
The following demonstration illustrates how students can leverage local LLMs to construct a generative AI-powered assistant:
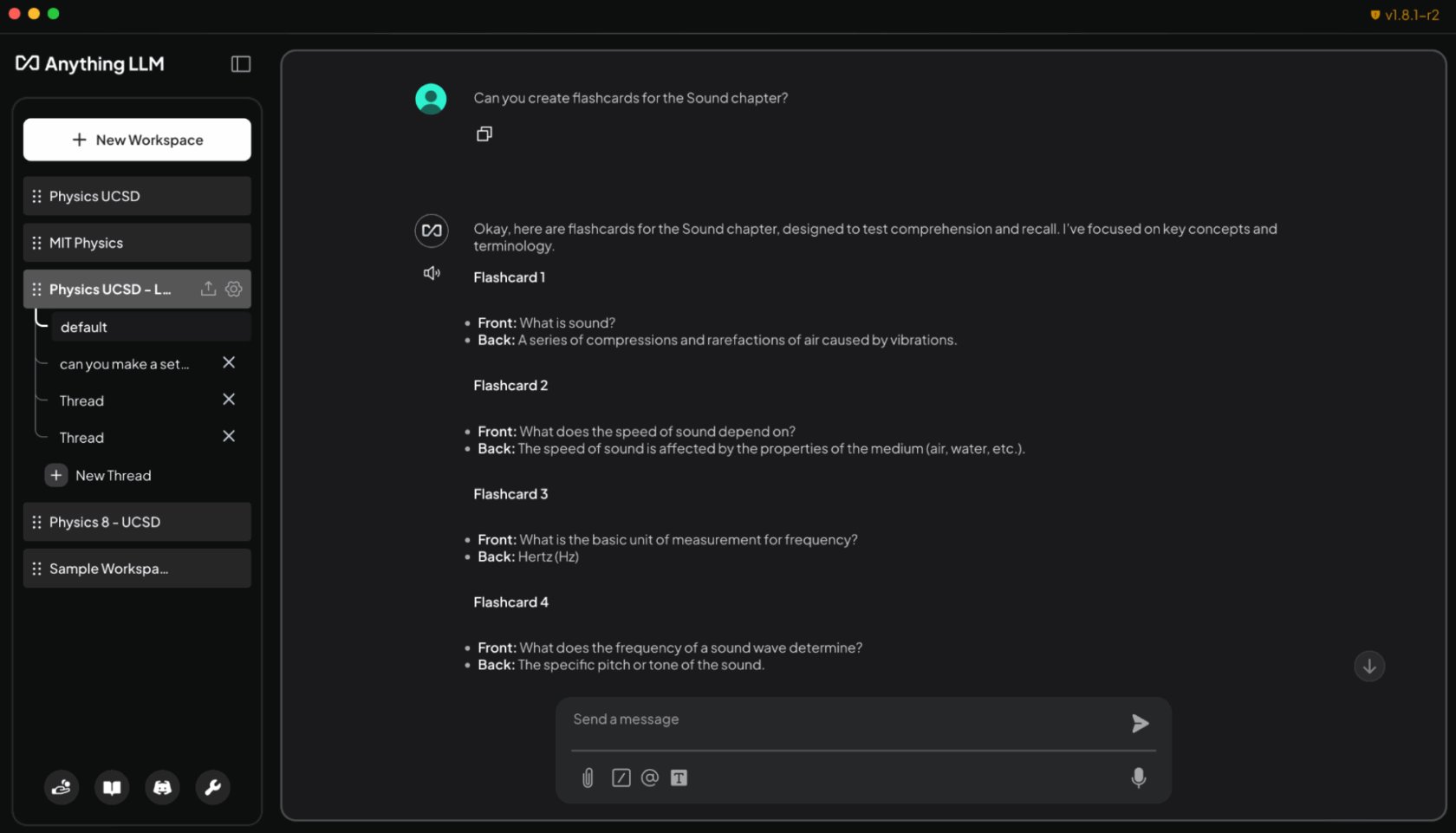 AnythingLLM, when run on an RTX PC, converts study materials into interactive flashcards, effectively creating a personalized AI tutor.
AnythingLLM, when run on an RTX PC, converts study materials into interactive flashcards, effectively creating a personalized AI tutor.
An accessible approach involves AnythingLLM, which supports document uploads, custom knowledge bases, and conversational interfaces. This makes it a versatile tool for individuals seeking to develop a customizable AI for research, projects, or daily activities. RTX acceleration further enhances response speeds.
Loading syllabi, assignments, and textbooks into AnythingLLM on RTX PCs provides students with an adaptive, interactive study companion. The agent can assist with tasks via text or speech, such as:
- Generating flashcards from lecture slides: “Create flashcards from the Sound chapter lecture slides. Put key terms on one side and definitions on the other.”
- Answering contextual questions related to their materials: “Explain conservation of momentum using my Physics 8 notes.”
- Developing and grading quizzes for exam preparation: “Create a 10-question multiple choice quiz based on chapters 5-6 of my chemistry textbook and grade my answers.”
- Providing step-by-step solutions for challenging problems: “Show me how to solve problem 4 from my coding homework, step by step.”
Outside academic settings, hobbyists and professionals can utilize AnythingLLM for certification preparation in new fields or similar objectives. Local execution on RTX GPUs guarantees rapid, private responses without subscription fees or usage restrictions.
Project G-Assist Can Now Control Laptop Settings
Project G-Assist functions as an experimental AI assistant, enabling users to tune, control, and optimize gaming PCs using straightforward voice or text commands, eliminating the need to navigate complex menus. A new G-Assist update is scheduled for release soon via the home page of the NVIDIA App.
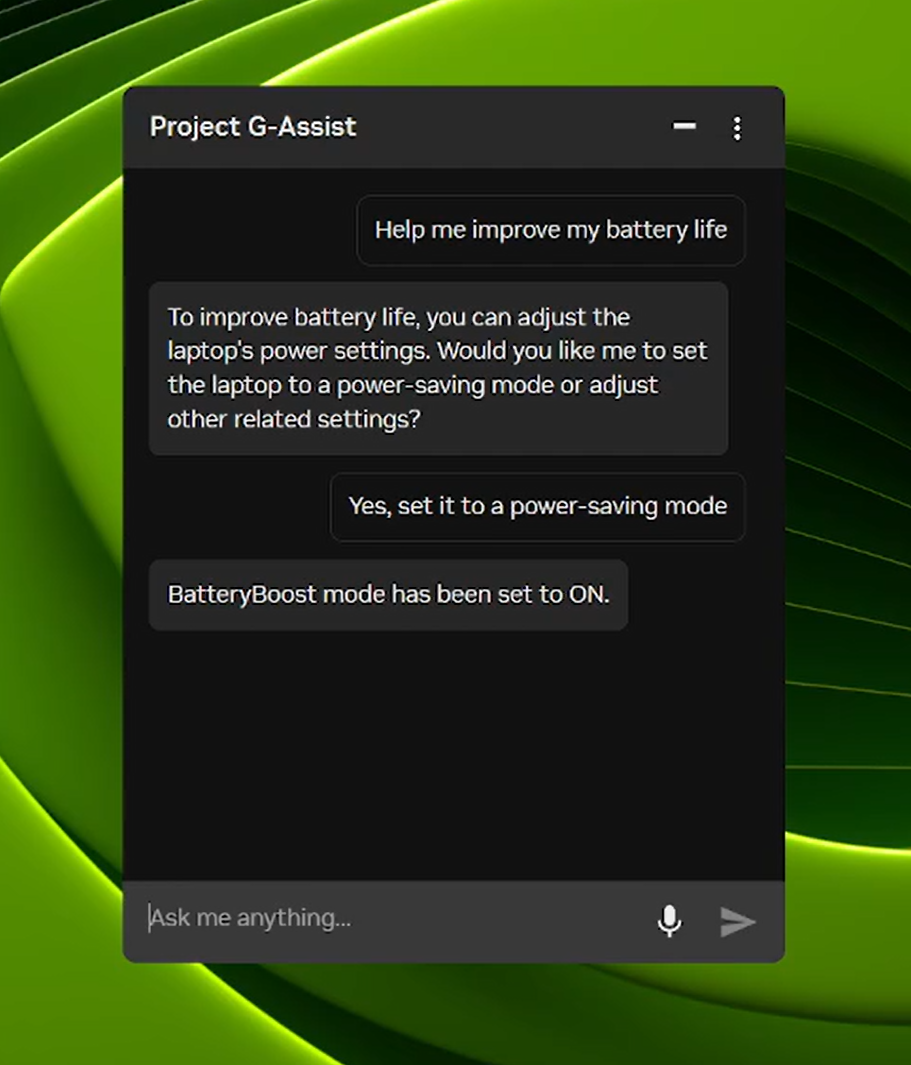 Project G-Assist assists users in tuning, controlling, and optimizing their gaming PCs using simple voice or text commands.
Project G-Assist assists users in tuning, controlling, and optimizing their gaming PCs using simple voice or text commands.
Expanding on its updated, more efficient AI model and support for most RTX GPUs released in August, the latest G-Assist update introduces commands for adjusting laptop settings, such as:
- Laptop-optimized app profiles: Automatically configure games or applications for efficiency, quality, or a balanced mode when laptops are not charging.
- BatteryBoost control: Enable or modify BatteryBoost to prolong battery life while maintaining smooth frame rates.
- WhisperMode control: Reduce fan noise by up to 50% when desired, and revert to full performance when not.
Project G-Assist also offers extensibility. The G-Assist Plug-In Builder allows users to create and customize G-Assist functionality by adding new commands or integrating external tools through simple plugins. Additionally, the G-Assist Plug-In Hub provides an easy way to discover and install plugins to broaden G-Assist’s capabilities.
The G-Assist GitHub repository contains resources for getting started, including sample plug-ins, detailed instructions, and documentation for developing custom functionalities.
#ICYMI — The Latest Advancements in RTX AI PCs
Ollama Performance Boost on RTX
Recent updates to Ollama feature optimized performance for OpenAI’s gpt-oss-20B, accelerated Gemma 3 models, and improved model scheduling to mitigate memory issues and enhance multi-GPU efficiency.
Llama.cpp and GGML Optimized for RTX
The newest updates provide faster, more efficient inference on RTX GPUs. These include support for the NVIDIA Nemotron Nano v2 9B model, Flash Attention enabled by default, and CUDA kernel optimizations.
Project G-Assist Update Released
The G-Assist v0.1.18 update is available for download through the NVIDIA App. This update introduces new commands for laptop users and improves answer quality.
Windows ML With NVIDIA TensorRT for RTX Now Generally Available
Microsoft has released Windows ML with NVIDIA TensorRT for RTX acceleration. This offers up to 50% faster inference, simplified deployment, and support for LLMs, diffusion, and other model types on Windows 11 PCs.
NVIDIA Nemotron Powers AI Development
The NVIDIA Nemotron collection, comprising open models, datasets, and techniques, drives AI innovation across various applications, from generalized reasoning to industry-specific solutions.
Connect with NVIDIA AI PC on Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and X. Stay updated by subscribing to the RTX AI PC newsletter.
Follow NVIDIA Workstation on LinkedIn and X.
Refer to the notice concerning software product information.