Generative and agentic AI applications are transforming modern workflows on personal computers. Examples include tailoring chatbots for product support or developing personal assistants for schedule management. A common challenge involves ensuring small language models consistently provide highly accurate responses for specialized agentic tasks.
Fine-tuning addresses this challenge.
Unsloth, a widely adopted open-source framework for LLM fine-tuning, offers an accessible method for customizing models. It is optimized for efficient, low-memory training on NVIDIA GPUs, encompassing GeForce RTX desktops and laptops, RTX PRO workstations, and DGX Spark, a compact AI supercomputer.
The recently announced NVIDIA Nemotron 3 family of open models, data, and libraries also provides a strong foundation for fine-tuning. Nemotron 3 features highly efficient open models, suitable for agentic AI fine-tuning.

Customizing AI Models
Fine-tuning involves providing an AI model with focused training. By using examples relevant to a specific topic or workflow, the model enhances its accuracy by learning new patterns and adapting to the intended task.
The choice of fine-tuning method depends on the extent of modification desired for the original model. Developers can select from three primary fine-tuning approaches based on their objectives:
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (e.g., LoRA or QLoRA)
- How it works: This method updates only a small portion of the model, resulting in faster and more cost-effective training. It offers an efficient way to improve a model without making drastic alterations.
- Target use case: Applicable across most scenarios where full fine-tuning would traditionally be used, such as incorporating domain knowledge, boosting coding accuracy, adapting models for legal or scientific applications, refining reasoning, or aligning tone and behavior.
- Requirements: A small to medium-sized dataset (100-1,000 prompt-sample pairs).
Full Fine-Tuning
- How it works: All of the model’s parameters are updated, which is useful for instructing the model to adhere to specific formats or styles.
- Target use case: Advanced applications, including developing AI agents and chatbots that must offer assistance on a particular subject, operate within defined constraints, and respond in a specific manner.
- Requirements: A large dataset (1,000+ prompt-sample pairs).
Reinforcement Learning
- How it works: This technique adjusts model behavior using feedback or preference signals. The model learns through interaction with its environment, using feedback to improve over time. This is an advanced method that integrates training and inference, and it can be combined with parameter-efficient and full fine-tuning techniques. Refer to Unsloth’s Reinforcement Learning Guide for more information.
- Target use case: Enhancing model accuracy in specialized fields like law or medicine, or creating autonomous agents capable of orchestrating actions on behalf of a user.
- Requirements: A process that includes an action model, a reward model, and an environment for the model to learn from.
VRAM requirements also vary by method. The following chart summarizes the requirements for each fine-tuning method on Unsloth.
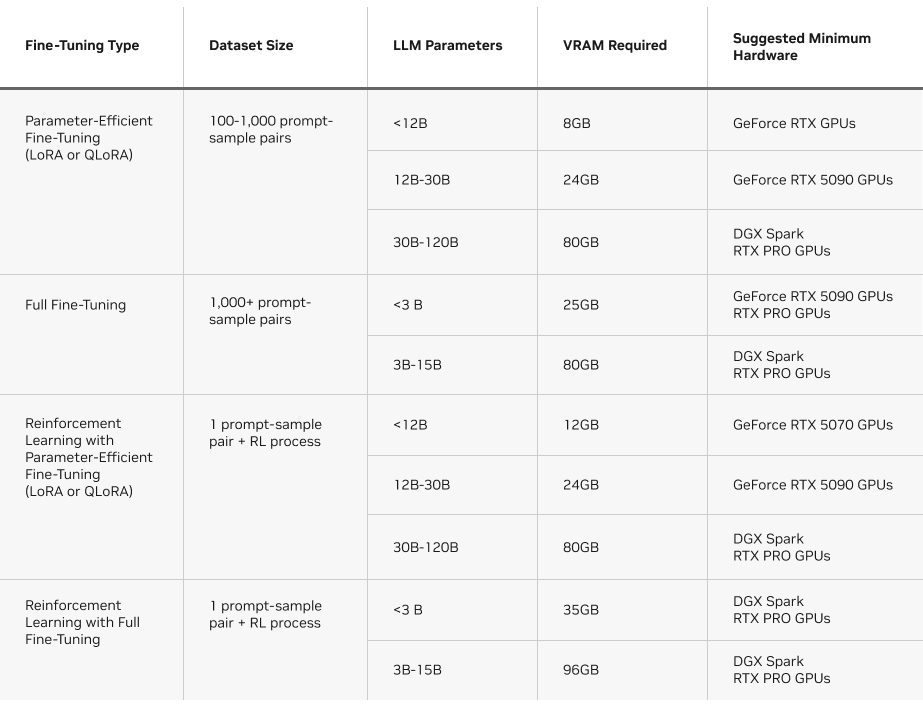 Fine-tuning requirements on Unsloth.
Fine-tuning requirements on Unsloth.
Unsloth: Accelerating Fine-Tuning on NVIDIA GPUs
LLM fine-tuning is a demanding workload, requiring significant memory and computational power due to billions of matrix multiplications involved in updating model weights during each training step. NVIDIA GPUs are essential for efficiently and rapidly completing such heavy parallel workloads.
Unsloth excels in this area by converting complex mathematical operations into optimized, custom GPU kernels to speed up AI training.
Unsloth enhances the performance of the Hugging Face transformers library by 2.5x on NVIDIA GPUs. These GPU-specific optimizations, combined with Unsloth’s user-friendly nature, make fine-tuning accessible to a wider range of AI enthusiasts and developers.
The framework is designed and optimized for NVIDIA hardware, from GeForce RTX laptops to RTX PRO workstations and DGX Spark, ensuring peak performance while minimizing VRAM consumption.
Unsloth provides comprehensive guides for getting started, managing various LLM configurations, hyperparameters, and options, along with example notebooks and step-by-step workflows.
Some Unsloth guides include:
- Fine-Tuning LLMs With NVIDIA RTX 50 Series GPUs and Unsloth
- Fine-Tuning LLMs With NVIDIA DGX Spark and Unsloth
Instructions for installing Unsloth on NVIDIA DGX Spark are available. A deep dive into fine-tuning and reinforcement learning on the NVIDIA Blackwell platform can be found in the NVIDIA technical blog.
For a practical local fine-tuning demonstration,
https://www.youtube.com/@matthew_berman
illustrates reinforcement learning running on an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5090 using Unsloth in the video below.
NVIDIA Nemotron 3 Family of Open Models: Now Available
The new Nemotron 3 family of open models, offered in Nano, Super, and Ultra sizes, is built on a hybrid latent Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture. This family introduces highly efficient open models with leading accuracy, making them ideal for developing agentic AI applications.
Nemotron 3 Nano 30B-A3B, currently available, represents the most compute-efficient model in the series. It is optimized for tasks such as software debugging, content summarization, AI assistant workflows, and information retrieval, all at low inference costs. Its hybrid MoE design offers:
- Up to 60% fewer reasoning tokens, significantly reducing inference expenses.
- A 1 million-token context window, enabling the model to retain substantially more information for extended, multi-step tasks.
Nemotron 3 Super is a high-accuracy reasoning model designed for multi-agent applications, while Nemotron 3 Ultra is intended for complex AI applications. Both are anticipated to be released in the first half of 2026.
NVIDIA also released an open collection of training datasets and advanced reinforcement learning libraries. Nemotron 3 Nano fine-tuning is supported on Unsloth.
Nemotron 3 Nano can be downloaded from Hugging Face, or experimented with via Llama.cpp and LM Studio.
DGX Spark: A Compact AI Powerhouse
DGX Spark facilitates local fine-tuning and delivers impressive AI performance within a compact, desktop supercomputer, providing developers with more memory than a typical PC.
Based on the NVIDIA Grace Blackwell architecture, DGX Spark provides up to a petaflop of FP4 AI performance and includes 128GB of unified CPU-GPU memory. This capacity offers ample headroom for running larger models, longer context windows, and more demanding training workloads locally.
For fine-tuning, DGX Spark offers several advantages:
- Larger model sizes: Models exceeding 30 billion parameters often surpass the VRAM capacity of consumer GPUs but operate comfortably within DGX Spark’s unified memory.
- More advanced techniques: Full fine-tuning and reinforcement-learning-based workflows, which require greater memory and higher throughput, run considerably faster on DGX Spark.
- Local control without cloud queues: Developers can execute compute-intensive tasks locally, avoiding waits for cloud instances or the management of multiple environments.
DGX Spark’s capabilities extend beyond LLMs. High-resolution diffusion models, for instance, frequently demand more memory than a standard desktop can provide. With FP4 support and extensive unified memory, DGX Spark can generate 1,000 images in mere seconds and maintain higher throughput for creative or multimodal pipelines.
The table below illustrates performance for fine-tuning the Llama family of models on DGX Spark.
 Performance for fine-tuning Llama family of models on DGX Spark.
Performance for fine-tuning Llama family of models on DGX Spark.
As fine-tuning workflows evolve, the new Nemotron 3 family of open models provides scalable reasoning and long-context performance, optimized for RTX systems and DGX Spark.
Information on how DGX Spark enables intensive AI tasks is available.
Recent Advancements in NVIDIA RTX AI PCs
FLUX.2 Image-Generation Models Released, Optimized for NVIDIA RTX GPUs
New models from Black Forest Labs are available in FP8 quantizations, which reduce VRAM and boost performance by 40%.
Nexa.ai Expands Local AI on RTX PCs With Hyperlink for Agentic Search
The new on-device search agent achieves 3x faster retrieval-augmented generation indexing and 2x faster LLM inference, indexing a dense 1GB folder in approximately four to five minutes, down from about 15 minutes. Additionally, DeepSeek OCR now runs locally in GGUF via NexaSDK, enabling plug-and-play parsing of charts, formulas, and multilingual PDFs on RTX GPUs.
Mistral AI Unveils New Model Family Optimized for NVIDIA GPUs
The new Mistral 3 models are optimized from cloud to edge and are available for rapid, local experimentation through Ollama and Llama.cpp.
Blender 5.0 Features HDR Color and Significant Performance Gains
This release includes ACES 2.0 wide-gamut/HDR color, NVIDIA DLSS for up to 5x faster hair and fur rendering, improved handling of large geometry, and motion blur for Grease Pencil.
NVIDIA AI PC content is available on Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and X. Follow NVIDIA Workstation on LinkedIn and X.

